tomcat-如何建立连接,获取远程请求
学习探讨tomcat如何建立网络连接协议,并处理客户端过来的请求
建立网络连接,指定http1.1通信协议
tomcat在创建时,会创建连接对象,负责处理客户端的请求,基于socket
connector 连接 protocol 协议 endpoint终端 socket插座,端口连接
创建初始化,对象创建顺序
connector > protocol > endpoint > socket
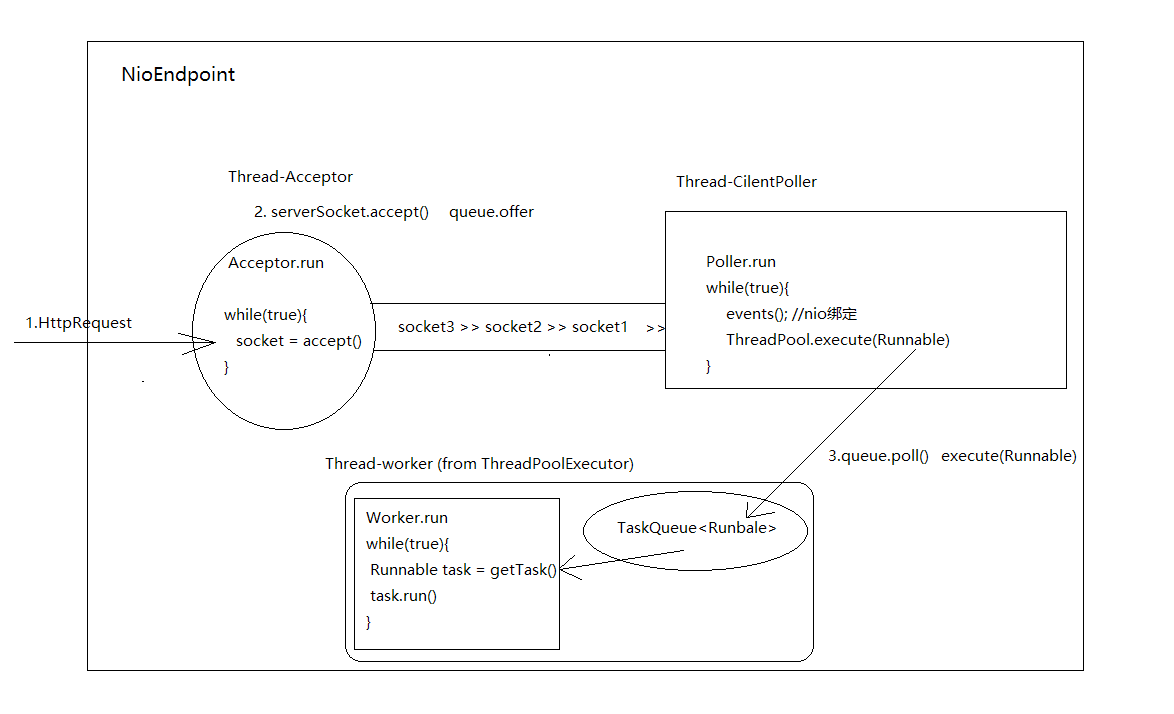
接收请求创建任务
acceptor.socket.acceptor()->
socketWrapper(携带通信信息)
-> poller(socketWrapper)
-> execute(socketWrapper) 创建线程
创建连接器
Conector类
org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector
空参构造connector() -> connector(http/1.1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
/**
* Defaults to using HTTP/1.1 NIO implementation.
*/
public Connector() {
this("HTTP/1.1");
}
指定通信协议http11
类
org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol
-> new Http11NioProtocol()
1
2
3
public Http11NioProtocol() {
super(new NioEndpoint());
}
指定服务终端处理模型非阻塞nio
类
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint
-> new NioEndPoint()
创建之后如何被启动?见springboot启动tomcat方式
终端处理线程和线程池初始化
启动之后
NioEndpoint执行bind()方法,
一些初始化,绑定端口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
@Override
public void bind() throws Exception {
initServerSocket();
setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(1));
// Initialize SSL if needed
initialiseSsl();
selectorPool.open(getName());
}
//socket相关 initServerSocket()具体如下
// Separated out to make it easier for folks that extend NioEndpoint to
// implement custom [server]sockets
protected void initServerSocket() throws Exception {
//.......
//根据平台不同,反回具体底层类对象(windows,linux,unix)
serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open();
socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket());
//绑定地址和端口号
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(), getPortWithOffset());
serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());
//.......
}
NioEndpoint初始化之后,调用start()执行startInternal()
代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// Create worker collection
if (getExecutor() == null) {
//创建线程池
createExecutor();
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
// Start poller thread
// 创建客户端队列(客户端过来的请求)
poller = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(poller, getName() + "-ClientPoller");
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
//创建接收远程请求线程
startAcceptorThread();
初始化线程池配置
-> createExecutor() 用于处理用户请求
指定 备用线程,对大线程数,队列类型,超时时间,和线程工厂
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public void createExecutor() {
internalExecutor = true;
TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority());
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf);
taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor);
}
创建Poller线程
1
2
3
4
5
poller = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(poller, getName() + "-ClientPoller");
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
创建Acceptor线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
protected void startAcceptorThread() {
acceptor = new Acceptor<>(this);
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor";
acceptor.setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptor, threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}
处理请求的相关对象(线程)
Acceptor
类
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.Acceptor
Acceptor 负责循环等待远程请求,将请求以socket形式携带信息,调用setSocketOptions()将socket包装配置为socketWrapper,
setSocketOptions: 对socket包装处理配置,使用poller对象注册到队列,让poller线程做后续的处理
Acceptor 类的run方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
//......以下省略部分代码
try {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
// 一直循环等待远程请求
while (!stopCalled) {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server socket
// 1 接收请求
socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// 2 处理请求,setSocketOptions() 内部调用poller 将新请求任务放入队列
if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) {
endpoint.closeSocket(socket);
}
}
} finally {
stopLatch.countDown();
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}
Poller
类
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller
Poller负责接收包装后的socket请求,放入队列,
并在run方法中循环去poll()请求任务,将与流读写有关的组件IOChannel Selector socketWrapper 绑定关联
再通过selector获取selectionKeys
迭代循环获取对应的socket,提交任务(线程),线程读写处理socketWrapper等后续操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public void run() {
// Loop until destroy() is called
while (true) {
// events()方法 poller队列任务处理 将IOChannel Selector socketWrapper 关联
hasEvents = events();
//......省略
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch
// 非阻塞io api 任务处理
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
if (socketWrapper != null) {
// 如果有等待处理的任务,则处理
processKey(sk, socketWrapper);
//processKey内部会调用processSocket方法,最终用线程池提交任务
}
}
// Process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
}
getStopLatch().countDown();
}
调用线程池处理请求
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = null;
if (processorCache != null) {
sc = processorCache.pop();
}
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
Executor executor = getExecutor(); //获取线程池
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
executor.execute(sc); //最终通过线程池处理配置后的请求
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
events队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events =
new SynchronizedQueue<>(); //事件队列(socket请求)
//注册请求到队列
public void rigister(final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper)
{
event = new PollerEvent(socketWrapper, OP_REGISTER);
addEvent(event);
}
private void addEvent(PollerEvent event) {
events.offer(event);
if (wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
其他
events()绑定及后面的 processSocket()最终提交实际处理任务到线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
/**
* Processes events in the event queue of the Poller.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if some events were processed,
* <code>false</code> if queue was empty
*/
public boolean events() {
boolean result = false;
PollerEvent pe = null;
for (int i = 0, size = events.size(); i < size && (pe = events.poll()) != null; i++ ) {
result = true;
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = pe.getSocketWrapper();
SocketChannel sc = socketWrapper.getSocket().getIOChannel();
int interestOps = pe.getInterestOps();
if (sc == null) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.nullSocketChannel"));
socketWrapper.close();
} else if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) {
try {
//注册绑定
sc.register(getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper);
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x);
}
} else {
final SelectionKey key = sc.keyFor(getSelector());
if (key == null) {
// The key was cancelled (e.g. due to socket closure)
// and removed from the selector while it was being
// processed. Count down the connections at this point
// since it won't have been counted down when the socket
// closed.
socketWrapper.close();
} else {
final NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment();
if (attachment != null) {
// We are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter.
try {
int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps;
attachment.interestOps(ops);
key.interestOps(ops);
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper);
}
} else {
cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper);
}
}
}
if (running && !paused && eventCache != null) {
pe.reset();//清空任务socketWrapper
eventCache.push(pe);
}
}
return result;
}
setSocketOptions 中的socket任务注册
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = null;
try {
// Allocate channel and wrapper
NioChannel channel = null;
if (nioChannels != null) {
channel = nioChannels.pop();
}
//...... 部分省略
NioSocketWrapper newWrapper = new NioSocketWrapper(channel, this);
socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
poller.register(socketWrapper);
return true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.socketOptionsError"), t);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
if (socketWrapper == null) {
destroySocket(socket);
}
}